
Quick actions
Shortcuts to AI jobs positioned inline alongside familiar options, or generated dynamically for a personalised experience.
Key characteristics
High findability, can be placed among non-AI options
Great at showing (and educating about) AI capabilities
Personalised dynamic actions support retention, users come back because workflow feels faster and easier
About
A quick action is simply a button or menu option that triggers an AI task. The less extra input it needs, the more useful it tends to be.
As a rule of thumb, most common AI use should start from a quick action. Users shouldn’t need prompt skills to do common jobs like explain, modify, review, or synthesize.
Quick actions are the easiest way to onboard AI functionality, as they use a decades-old pattern of “click a button, expect an action.”
Types of actions
1. Static actions
Static actions are most common AI tasks accessible like any standard function, like copy or paste. They should be predictable and stay in the same place. Imagine if the “Rename” button disappeared or got moved frequently.
To earn their spot, static actions need two things: people should reach for them often in that tool or context, and AI should be reliably good at the job.

Notion is a good example. When you open the menu on selected text, you get text-related actions
2. Dynamic actions
Dynamic actions are tasks created by AI itself. By understanding user context, AI can create bespoke quick actions for specific users to speed up their workflow.
Within the interface, dynamic actions appear as suggestions. For further reading, see Suggest in context
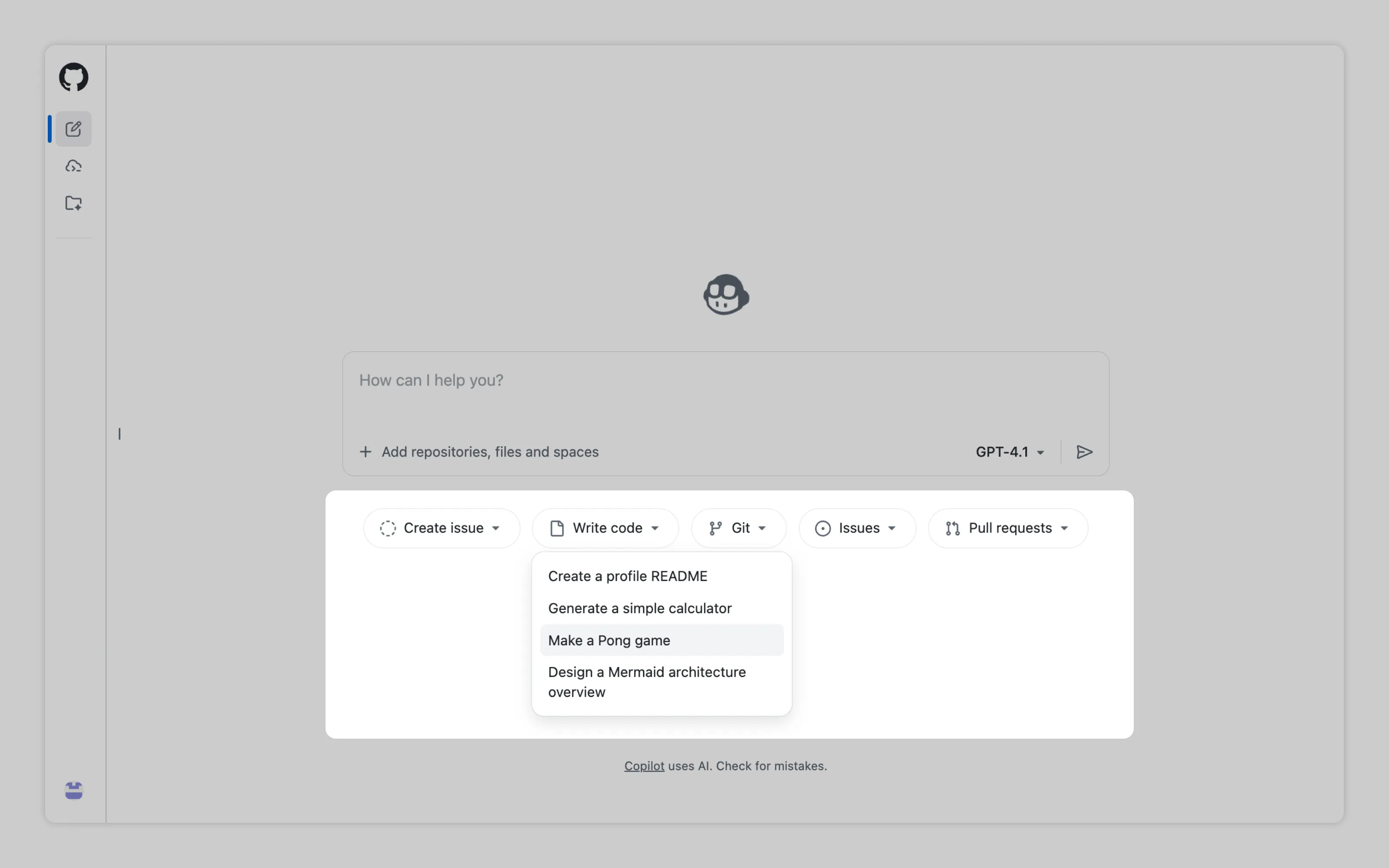
GitHub Copilot is a good example. Since it can read the user’s project, it can offer actions that match that codebase.
Or email us at hello@studiolaminar.com
