
Open input
Open ended input for requests beyond predefined actions
Key characteristics
Handles any task, but costs more effort than quick actions
Cognitive load can be reduced with starter templates
Gets faster and more consistent with tone/length/format parameters
About
Technically, every AI action can be triggered via open input by telling the AI what to do. The prompting process however is:
Slow: it’s much quicker to click a button than to write an entire request.
Hard: users must understand what AI can do and think about how to phrase the request.
Imprecise: AI works best with prompts written in a particular way. Users without that knowledge might have a hard time getting AI to understand them.
That’s why prompting should be reserved for unique, specific tasks, while common, repeatable tasks should be handled through AI quick actions.
For example, it makes sense to write detailed instructions for AI about what key information should be added to a text. But if the goal is simply to make the text shorter, it’s much faster to highlight it and select the “Shorten” option from a menu.
The open input pattern covers “one-shot” prompts for tasks. For continuous interaction with AI, see the Chat workflow pattern.
How to support tasking AI via open input
1. Suggest starting points and templates
The best inputs don't require prompting at all. Use data from your tool to propose context rich ready-made solutions that execute tasks or populate prompts with one click, eliminating blank-page paralysis. Two types of patterns can be utilised to help users get started:
Display common or contextually relevant tasks as buttons near the open input. Clicking them instantly fills the input with a prepared prompt and starts generation. Users get immediate value without typing a single word.
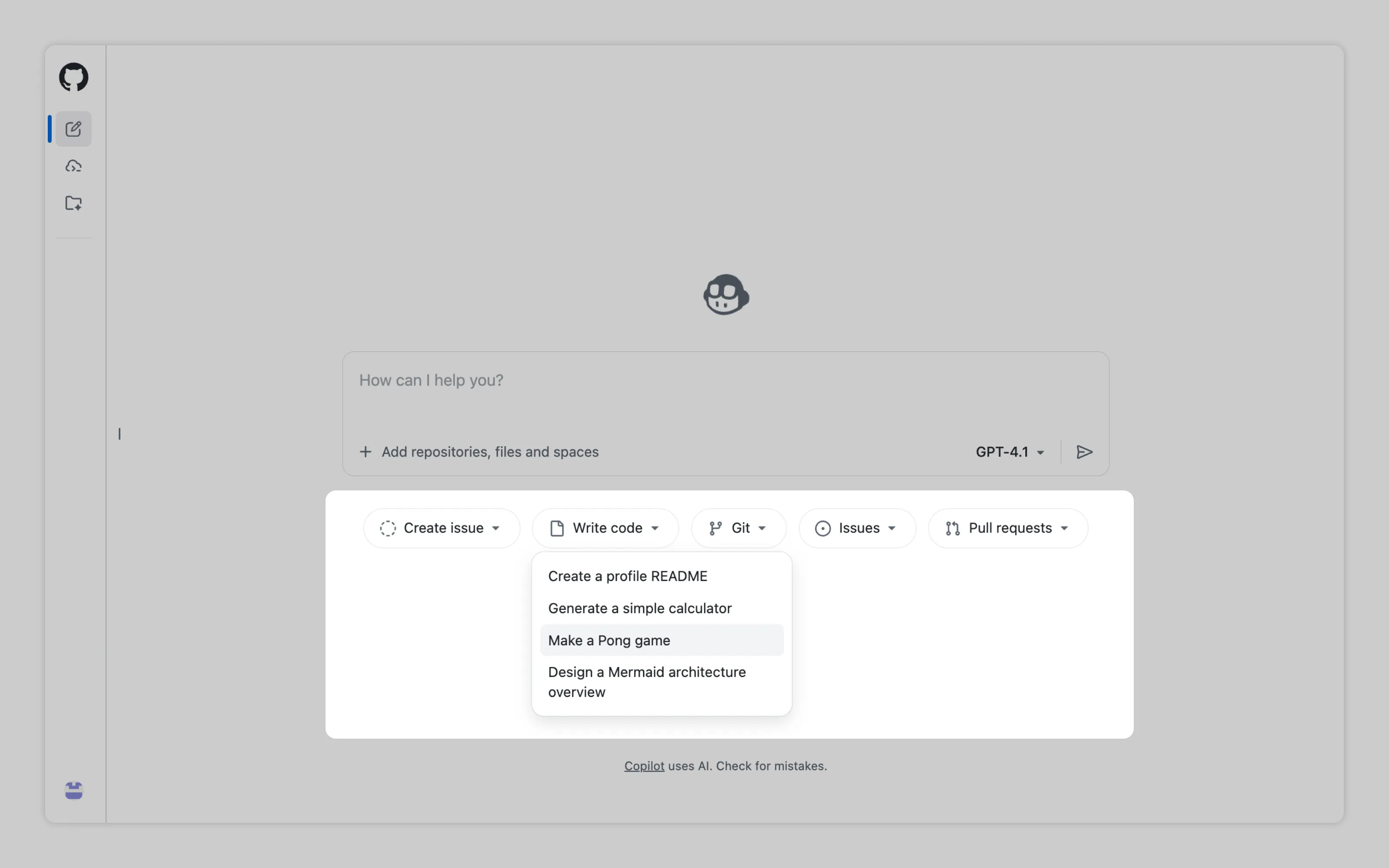
GitHub uses repository contents to suggest ready-made actions like writing a README for users profile
If particular requests are repeatable but still require open input, you can provide a template for users to fill in. Bonus points if the template can be triggered from the place where users would naturally look to perform the task in question.

GitHub provides a “Draft with Copilot” button within the “Create sub-issue” menu. When clicked, it fills the open input with a pre-written prompt (a template).
2. Capture context
Users should never have to manually provide context to AI if it already exists within the tool. For example, if users want part of the text modified, they shouldn’t have to copy and paste it into an AI chat. Instead, they can simply highlight the text and ask AI to modify it. Read more at context pointing
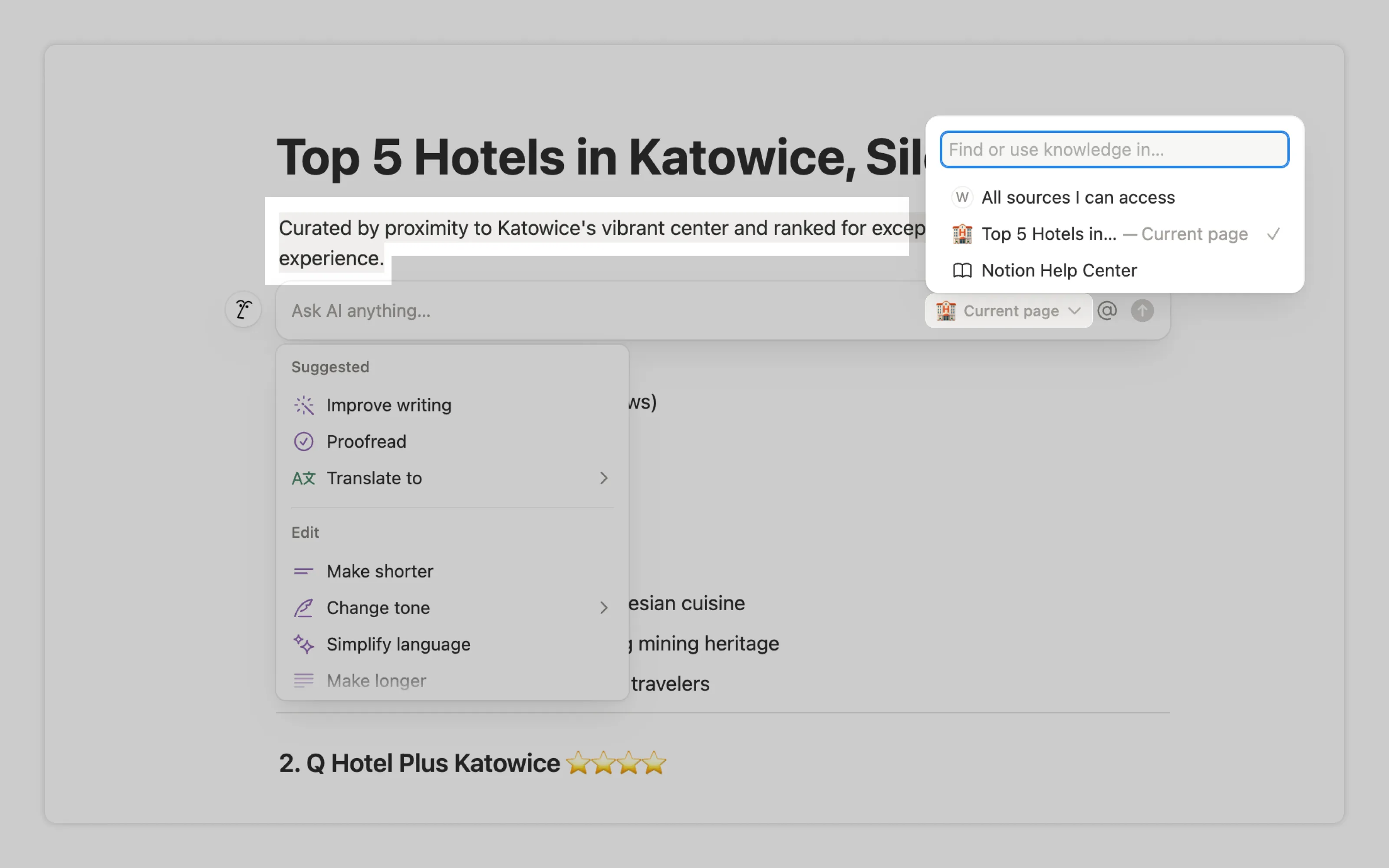
Notion modifies only the selected text while allowing users to include additional context. In this case, it lets them choose which data source the AI can reference.
3. Provide parameters
If a task has a few common options, or a setting that maps well to a slider, don’t make users spell it out in the prompt. Give them dropdowns and sliders for things like tone or length. It’s faster and more consistent. Read more at the Parameters pattern.
4. Simplify writing itself
Use autocomplete to reduce typing. If your users are familiar with taging coworkers or insert variables in text, add triggers like @ or / that open a menu of common references or functions
Or email us at hello@studiolaminar.com
